Description
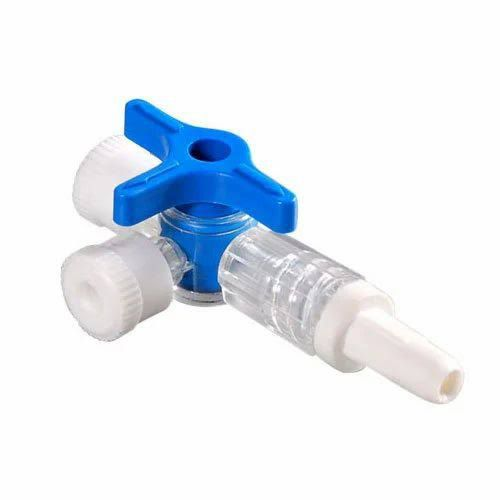
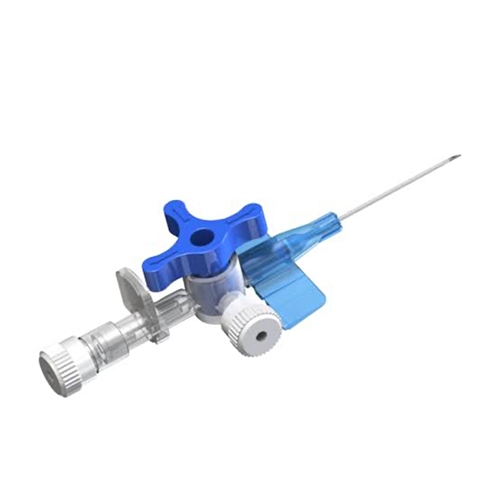
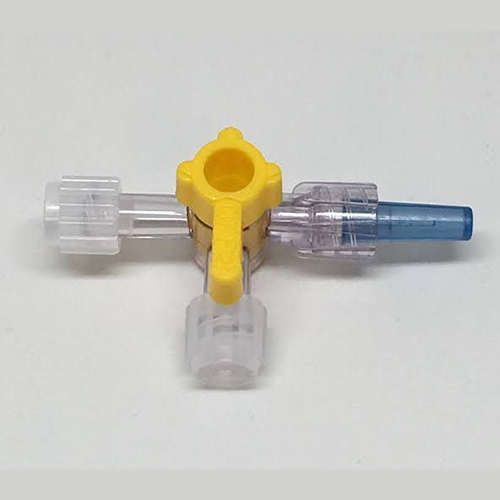
3 way stopcock standard a valve with three ports used in medical procedures. It controls fluid flow between ports by rotating a handle.
Features:
Three Ports: A regular 3-way stopcock has three openings, allowing fluids to move straight, turn right, or stop completely.
Rotating Handle: The handle rotates fully but stops every 90°. This lets you carefully select openings for fluid flow or shutoff.
Luer Lock or Luer Slip Connections: Standard connections ensure easy, secure attachment of the stopcock to syringes, tubes, or equipment.
Transparent Body: It’s made from clear polycarbonate, allowing you to see fluid flow and detect air bubbles easily.
Leak-proof Design: 3-way stopcock stops leaks, keeps fluids in place, ensures safety, and maintains normal fluid control.
Biocompatible Materials: Made from materials that won’t harm the body or react with fluids or medications they contact.
Pressure Rating: It means that the 3-way stopcock is built to handle different kinds of pressure, making it utilised for a wide range of tasks.
Sterilization Compatibility: Thoroughly clean them with steam or special gas to ensure they’re completely free of germs and dirt.
Usage:
- Medication Administration:3-way stopcock lets doctors give several meds or fluids via one IV.
- Blood Sampling: Providers can take blood samples without stopping the IV drip.
- Hemodynamic Monitoring:3-way stopcock for arterial lines: measure BP & take blood samples.
- Central Venous Pressure (CVP) Monitoring: It helps calculate the pressure in a large vein, crucial for managing fluids in critical patients.
- Fluid Management: Helps control the movement of dialysis fluid in and out during hemodialysis.
- Contrast Injection: Helps inject contrast dye in a controlled way during CT scans or MRIs.
- Fluid Distribution: Helps distribute fluids precisely in experiments.
- Sample Collection: Allows you to collect samples from a reaction without stopping the experiment.